Capital: Buenos Aires
Population: 38.4 million (UN, 2003)
Year of Independence: 1816, from Spain
Type of Government: Republic
GNP: $391 billion (2002 est.)
Natural Resources: fertile plains of the Pampas, lead, zinc, tin, copper, iron ore, manganese
Political Parties: Action for the Republic (AR); Alternative for a Republic of Equals (ARI); Front for a Country in Solidarity (Frepaso) [a four-party coalition]; Justicialist Party (PJ) [Peronist umbrella political organization]; Radical Civic Union (UCR); several provincial parties
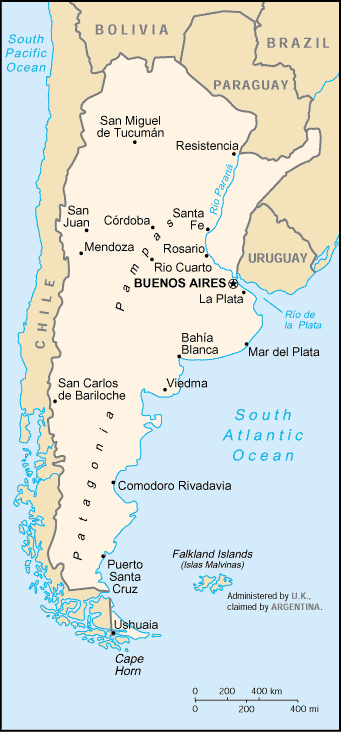
From the Andes Mountains in the west to its long Atlantic shoreline in the east, Argentina is a large, geographically diverse country. In the north, the climate is subtropical; the southern tip of Argentina is cold and windy. The Pampas plains in the central and northern parts of the country — home to the majority of the populous — are flat, grassy, and fertile, yielding much of the nation’s natural wealth in the form of livestock, wheat, corn, and grains. Most Argentineans are of European descent, and the country is largely Roman Catholic. It is also a very well-educated nation, with a 96 percent literacy rate. Since independence, Argentina has vacillated between civilian and military rule, including decades under the authoritarian administration of Juan Perón (president from 1946-55 and 1973-74) and a military junta that held power between 1976 and 1983. Recently, Argentina has experienced a calamitous economic crisis that has also undermined its political system. In 2001, Argentina defaulted on $155 billion of debt, prompting the resignation of President Fernando de la Rúa Bruno. Today, by some estimates, at least 40 percent of Argentina’s population, once predominately middle-class, lives below the nation’s poverty line. In the wake of de la Rúa’s resignation, Argentina saw a series of interim presidents, but stability now appears attainable. In May 2003, Néstor Kirchner assumed the presidency after his opponent, former president Carlos Saúl Menem (1989-99), withdrew from the scheduled runoff.
- Previous: Introduction
- Next: Bolivia