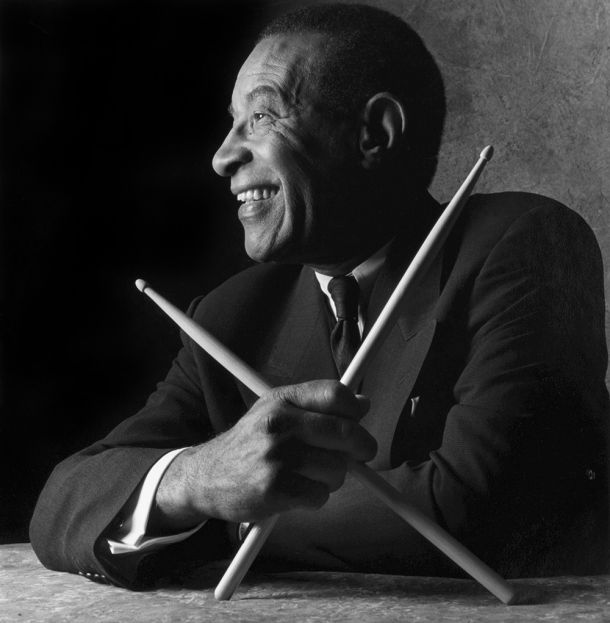
Max Roach is a musician whose far-reaching ambitions were inspired and challenged by the inequities of the society around him. His stunningly diverse seven-decade career marked him as one of the great musical artists of the 20th century and a pioneering cultural activist at times when the nation was steeped in racism. His career was an epic musical journey – from the revolutionary Jazz of the 1940s to the Civil Rights years, through experiments in hip hop, multi-media works, and beyond. This timeline details Max Roach’s life and the major milestones in his career.
Max Roach is a musician whose far-reaching ambitions were inspired and challenged by the inequities of the society around him. His stunningly diverse seven-decade career marked him as one of the great musical artists of the 20th century and a pioneering cultural activist at times when the nation was steeped in racism. His career was an epic musical journey – from the revolutionary Jazz of the 1940s to the Civil Rights years, through experiments in hip hop, multi-media works, and beyond. This timeline details Max Roach’s life and the major milestones in his career.
A DRUMMER IS BORN
Max Roach is born in Newland, North Carolina, to Alphonso and Cressie Roach.
The Roach family moves to Bedford-Stuyvesant neighborhood in Brooklyn, New York.
Max Roach begins drumming at Concord Baptist Church Bible School, where his mother sang in the chorus and his aunt was a pianist. Through them, Roach learns to read music.
Roach is invited by Duke Ellington to sit in as substitute with the Duke Ellington Orchestra at the Paramount Theatre.
BEBOP INNOVATIONS
Max Roach first performs with the Dizzy Gillespie Quintet at the Onyx Club, helping to develop the bebop style.
Max Roach records with Charlie Parker and Dizzy Gillespie, as well as with Benny Carter Orchestra, Sarah Vaughn, Stan Getz, Don Byas, Bud Powell and others.
MILES DAVIS COLLABORATION
It was a busy year for Max Roach. He participates in the historic "Birth of the Cool" recording sessions led by Miles Davis. He performs in Paris with the Charlie Parker Quintet. This year, he also marries Mildred Wilkinson, with whom he has two children, Maxine and Daryl.
Roach attends Manhattan School of Music, majoring at first in percussion before switching to composition. He continues gigging professionally and recording with, among others, Charlie Parker, Thelonious Monk, Miles Davis, Sonny Stitt, Charles Mingus.
HIS FIRST SOLO WORK
Max Roach releases his first recorded solo work, "Drum Conversation." He also forms a quintet with Clifford Brown, along with Richie Powell, George Morrow and Harold Land (later replaced by Sonny Rollins).
Son Raoul born to Roach and singer Barbara Jai (Johnson). Max Roach/Clifford Brown group records first album, "Brown and Roach Incorporated."
Clifford Brown and band member Richie Powell die in car accident on Pennsylvania Turnpike on the way to a gig. Roach continues to perform and record in a variety of different groups, but struggles psychologically with the loss.
Notable recordings: "Max Roach in 3/4 Time;" "Max Roach plus 4."
Roach performs "Concerto for Max," by Peter Phillips, at the Monterey Jazz Festival. He also conducts his own compositions with the Carme Chamber Orchestra in Milan. Notable 1958 recordings include "Freedom Suite" (Sonny Rollins); "Deeds Not Words."
Max Roach records "Rich vs. Roach," featuring drum battles with Buddy Rich.
"WE INSIST! MAX ROACH'S FREEDOM NOW SUITE"
Roach composes and records - with Abbey Lincoln and an all-star group including Coleman Hawkins - the now-classic social-change themed, "We Insist! Max Roach's Freedom Now Suite."
"We Insist! Max Roach's Freedom Now Suite" is performed at the NAACP Annual Convention. "We Insist!" album is banned from being imported into South Africa. Other notable 1961 recordings: "Out Front" (Booker Little); "Drum Suite" (Slide Hampton); "Percussion Bitter Sweet."
Roach marries singer-songwriter Abbey Lincoln.
Roach composes original score for Japanese film, "The Black Sun."
Records "Drums Unlimited," an album featuring three solo drum compositions that deeply influence modern drumming, such as "The Drum Also Waltzes."
M'BOOM
Max Roach founds M'Boom, a ten-piece percussion ensemble. They record and tour widely, performing a unique blend of original compositions and jazz standards.
Roach records "Lift Every Voice" and Sing with The J.C. White Singers. He marries Janice Adams. They have twin daughters, Ayo and Dara.
Facing reduced opportunities for performance and major label recordings, Roach accepts appointment as Professor of Music and African American Studies, University of Massachusetts, Amherst.
Roach records "Force" with Archie Shepp.
Records "Streams of Consciousness" duo album with South African pianist Abdullah Ibrahim.
Forms the Max Roach Double Quartet, consisting of jazz quartet and string quartet. Notable 1979 recordings include: "One in Two, Two in One" (with Anthony Braxton); "Historic Concerts" (with Cecil Taylor); "Long March" (with Archie Shepp); "Pictures in a Frame;" M'Boom.
Records album "Chatahoochie Red," featuring "The dream / It's time," a solo performance over Martin Luther King Jr.'s "I have a dream" speech.
HIP HOP INNOVATIONS
Roach performs live at The Kitchen performance space in New York with hip-hop artist Fab Five Freddy, DJs and break dancers.
Roach records albums "Scott Free" and "Survivors." He is honored with the title of Jazz Master by the National Endowment for the Arts.
Records "Easy Winnings" with the Max Roach Double Quartet.
Composes an OBIE Award-winning score for "Shepard Sets," a collaboration with Sam Shepard.
ROACH RECEIVES GENIUS GRANT
Max Roach receives the "Genius Grant" from the MacArthur Foundation.
Premiere of "The Life and Life of Bumpy Johnson" with the San Diego Repertory Theater, a play by Amiri Baraka, with original music by Max Roach.
Records the Grammy-nominated duo album with Dizzy Gillespie, "Max and Dizzy."
Performs as drum soloist with the Atlanta Symphony Orchestra in Frederick Tillis' "Festival Journey." "To the Max!" performance, showcasing a broad range of Roach’s music, is broadcast on television.
Performs Henry Threadgill's "Mix for Orchestra" with the Boston Philharmonic Orchestra. Also records "Max Roach with the New Orchestra of Boston and The So What Brass Quintet."
Debut of the multimedia work, "Ju-Ju," at Lincoln Center, featuring M'Boom, Kit Fitzgerald, and the Donald Byrd Dance Group.
GRAMMY HALL OF FAME
Max Roach leads Percussion Summit at the Verona Arena, featuring M'Boom, Tony Williams and Ginger Baker. He performs original work of dance, music and spoken word, Degga with Toni Morrison and Bill T. Jones at Lincoln Center. He is also inducted into the Grammy Hall of Fame for the 1953 Jazz at Massey Hall recording.
ROACH'S FINAL ALBUM
Roach records his final album, "Friendship," a duo recording with Clark Terry. He also composes the score for "How to Draw a Bunny," a documentary about artist Ray Johnson.
Max Roach dies at age 83, in Manhattan, NY.