© Sacha Mirzoeff
Common Name: African Lion
Family: Felidae
Genus: Panthera
Species: leo
Size: Males average 48 inches in height and 78 inches in length. Females average 42 inches in height and 66 inches in length. The lion is the second largest feline after the tiger.
Weight: Males average 330 to 500 lbs. Females average 265 to 400 lbs.
Coat: Tawny yellow coat. Adult males have a thick mane of brown or black hair. Lions are the only cat species to have prominent physical differences between the two genders.
Habitat: Grassy plains, the savanna, open woodlands, and dense bush. African lions live in warm environments.
Diet: Lions tend to eat ungulates like impala, wildebeest, zebra, giraffe, and buffalo, though they can feed on smaller animals like hares, birds or reptiles. They also scavenge, taking other animals’ kills.
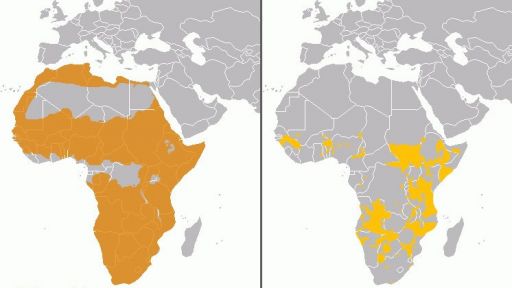
Geography: The African lion used to cover the majority of the continent, with the exception of the Saharan desert and the Congo basin’s dense rainforest. The lion has since disappeared from northern Africa and now lives mostly in the southern and eastern regions of the continent.
Population Health: Vulnerable (according to the IUCN)
Threats: Humans – Urban expansion results in habitat loss, fragmentation, and a decrease in food sources. People will also retaliate against lions that feed on domestic livestock or are aggressive toward neighboring human populations. Lions are threatened by disease and ecological changes to their environment.
Additional Facts:
- Lions were found in ancient Greece until approximately 100 AD. Lions even surface in Greek mythology. The first of Hercules’ twelve labors was to slay the giant lion of Nemea.
- While most cat species live a relatively solitary life, lions live in large groups referred to as prides. Prides generally consist of a number of females, their cubs, and one to three adult males.
- Females do almost all of the hunting. Lionesses tend to hunt at night and work in teams to stalk and ambush prey.
- Male lions are responsible for marking and protecting the pride’s territory.
- Lions mate perennially and produce a litter of two to three cubs. Cubs tend to remain with the mother for at least two years.
- When new males take over a pride, they often kill the existing cubs to get rid of that genetic strain and also so that the females will come into heat and allow the new males to sire their own cubs.
- Although lions are commonly referred to as “King of the Jungle,” this moniker is inaccurate. Lions live in grassy, open lands like savannas, not jungles.
- The Swahili word for lion, Simba, means “king”.